
It’s no secret that robots are becoming increasingly sophisticated. For decades, they’ve been an integral part of the manufacturing industry, performing production-line tasks with a speed and precision that’s lowered costs substantially.
But increasingly, the influence of robotics is being felt in other industries. Among the most exciting developments are happening in the world of healthcare. But exactly what kind of role are robots playing in that industry? Let’s take a look.
Revolutionizing Surgical Precision and Patient Outcomes
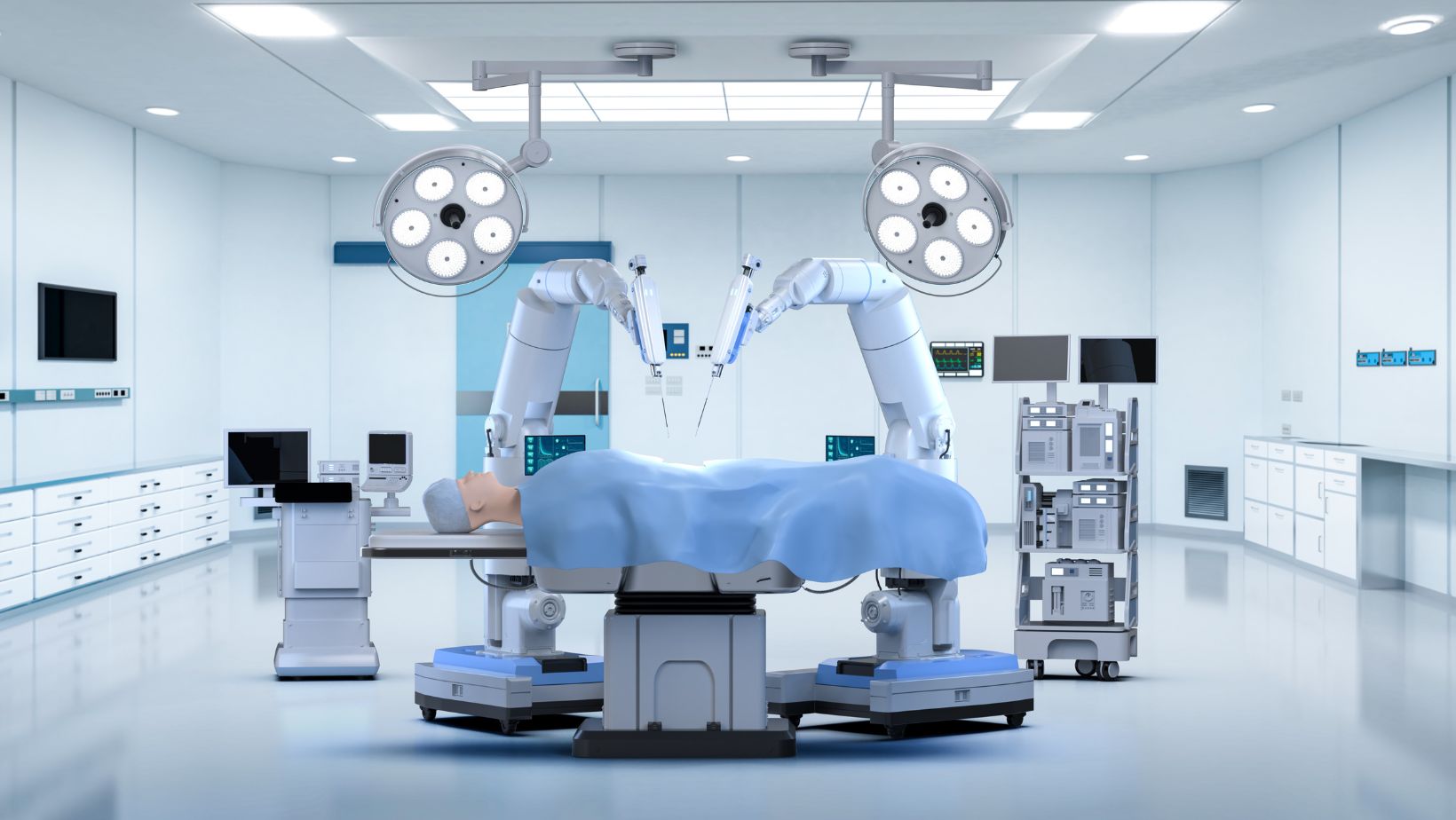
Surgical procedures rely on skilled operators who are able to perform precise incisions. With the help of specialized mechanical tools, a certain kind of surgeon can work in very sensitive areas of the body, like the heart and brain. Robotic systems are providing invaluable support to human surgeons.

They’re driving up the likelihood that a given procedure will be successful, they’re removing the need for invasive procedures (which increase the risk of an infection), and they’re leading to faster recovery times. All of this is good news not only from the point of view of the patient, but also from the point of view of the business, and of wider society.
In the United States, around a quarter of a million people die every year as a result of medical errors. But thanks to robotic systems, like the da Vinci robot, this figure is being driven down. This particular machine allows surgeons to manipulate robotic limbs, and get an unprecedented close-up view of the surgical site with the help of three-dimensional imaging hardware.
The Role of Connectors in Medical Robotics
Naturally, robots are built from collections of circuitry. For their various parts to interact properly, they’ll need to be maintained. This might require high-quality connectors, which allow (for example), instructions to be transmitted between the limbs of the machine, and the software that controls them.
These connectors might take many forms. They might offer convenient mate and un-mate features, corrosion-resistant materials, hybrid variations, and terminal blocks, all of which might be essential in medical robotics.
Enhancing Hospital Operations and Patient Care
As well as the important life-or-death procedures we’ve discussed thus far, robots might also play a role in automating routine medical tasks. They might, for example, dispense medicine, and control the release of automated treatments. They might be connected with hospital systems, which would allow for the collection of high-quality, high-precision patient data. All of these tasks can be performed well by humans – but by entrusting them to robots, we might allow healthcare professionals to focus on the aspects of care that might call for a human touch.
For example, Moxi is a robot designed to assist in transporting patient supplies, fetching PPE and medication, and delivering samples to laboratories.






